Taking your breath away…one macrophage, at a time.
This space will highlight literature relating to lung macrophages with emphasis on their functions during infections, repair, disease (resistance, tolerance, promotion) and mechanisms that drive those functions. I will also highlight their potential for innate immune memory.
2025
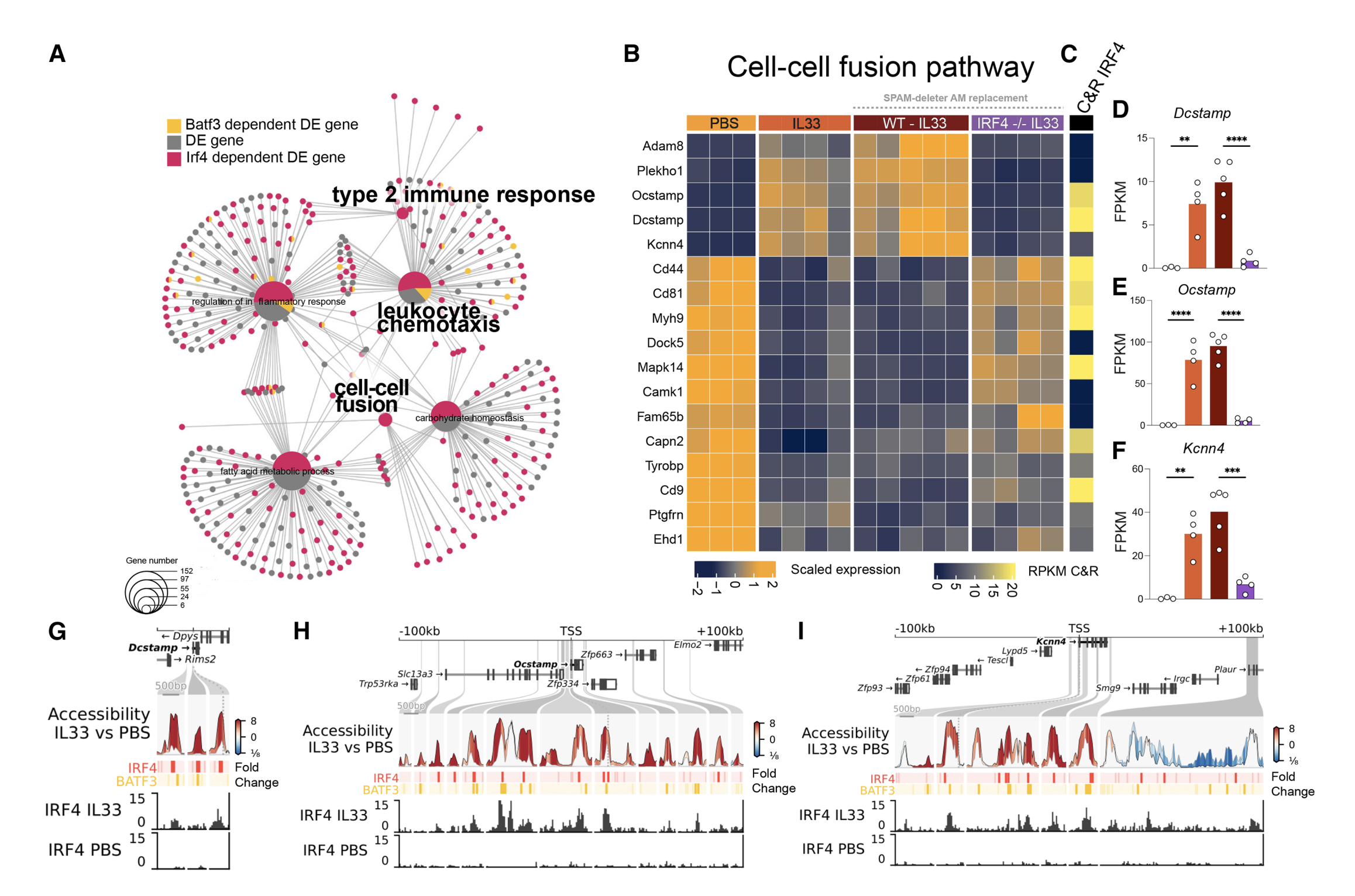
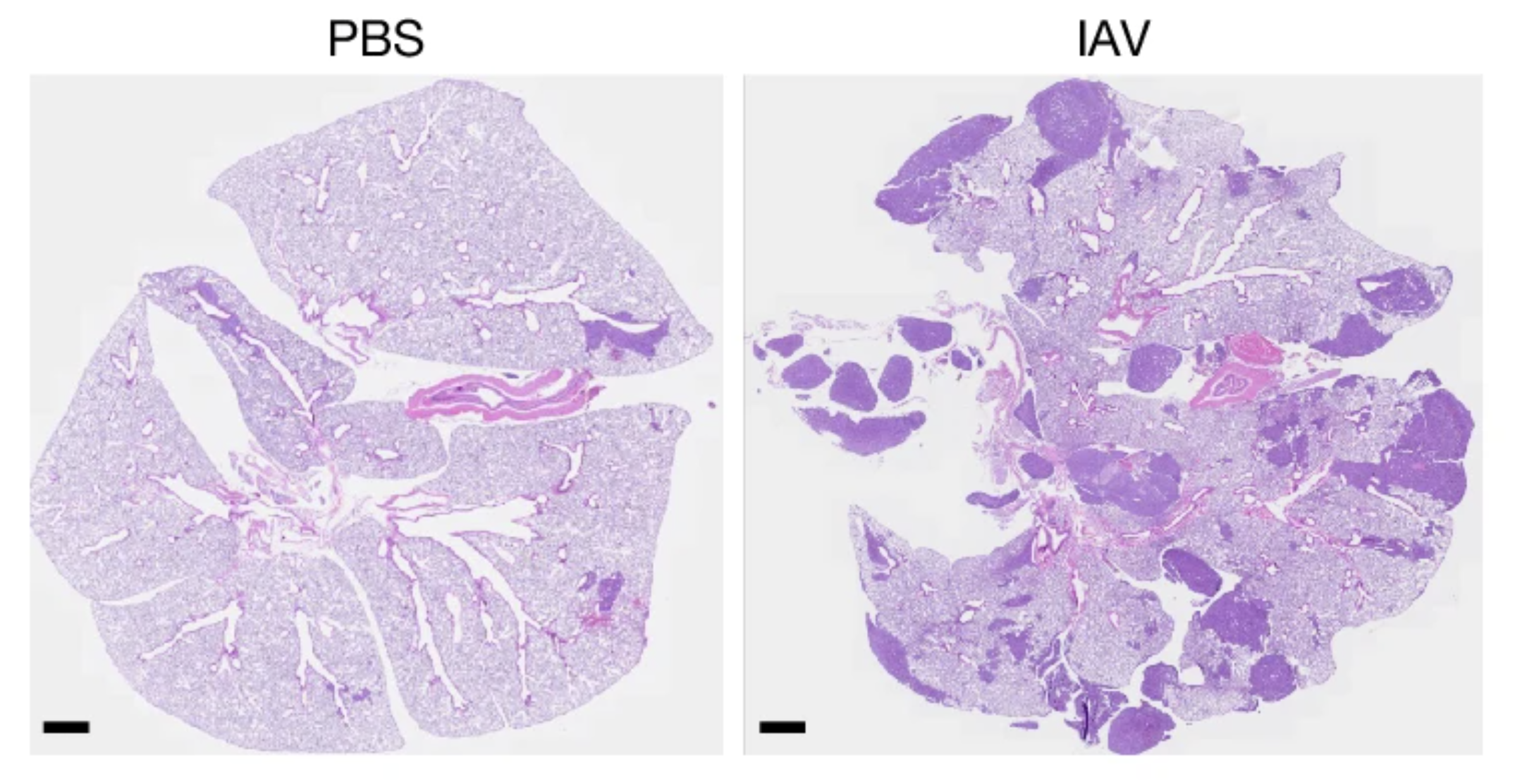
12. Verwaerde, Hastir and Lambrecht use a new SPAM-deleter model and HDM inoculation to show that IL-33-activated ILC2s reprogram tissue-resident AMs via IL-13 → IRF4, transiently suppressing the PPARγ homeostatic program and inducing chemokine release, cell recruitment, and multinucleated giant cell formation. Specific depletion of (only) tissue-resident AMs via SPAM-deleter mouse further reveals a reversible identity loss and not monocyte replacement, as a driver of type-2 lung pathology. [12/n]
11. Radhouani and Starkl use an EoCre-DTA model and epigenomic profiling, to show that skin S. aureus infection imprints a long-lasting eosinophil memory that rewires progenitors and exacerbates allergic sensitization and airway inflammation [11/n].
10. Jiang, Pan and Chen show that flu related deaths in aged cohorts are related to elevated Apolipoprotein D (ApoD) expression that drives extensive pulmonary mitophagy to attenuate type I IFN response, leading to promotion of influenza virus replication. [10/n]
9. Almanzar, Chiu and colleagues highlight the role of TRPV1+ sensory neurons in regulation of monocyte and neutrophil recruitment and contributions to host immunopathology during IAV infection via upregulation of ATF3 thereby controlling viral spread. [9/n]
8. Chia, DeGregori and colleagues report maladaptive consequences of a previous respiratory infection that awakens dormant cancer cells using two mouse models of metastasized breast cancer (that develop disseminated cancer cells) in the lungs via IL-6 and CD4+ T cells. [8/n]
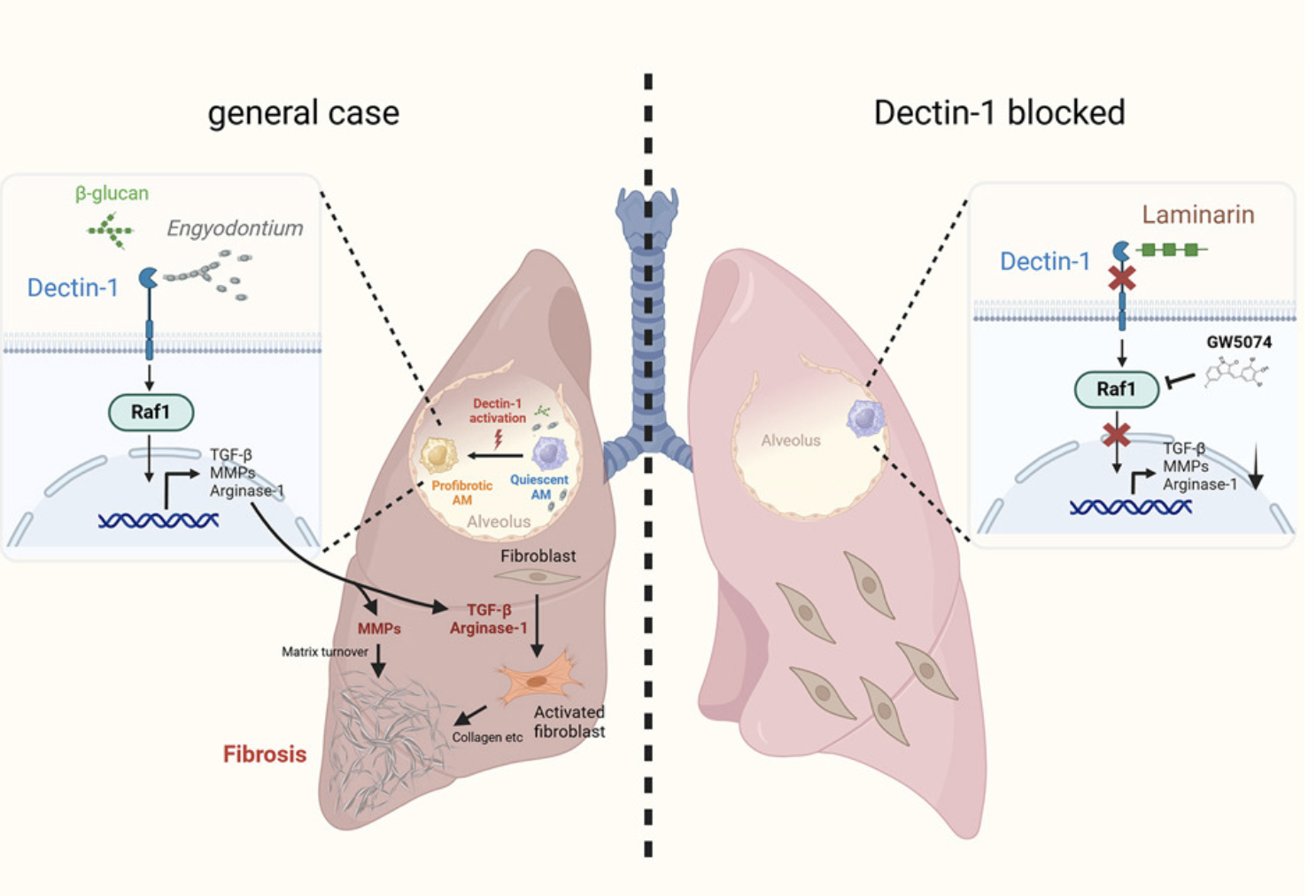
7. Qui, Tang and colleagues show how Dectin-1 signaling induces Arginase-1 / TGF-β AND and promotes profibrotic AMs via the Raf1-dependent pathway, bypassing CARD9 signaling and mono-macrophage chemotactic recruitment. [7/n]
6. Hoagland and Franklin show that macrophage-derived oncostatin M (OSM) is indispensable for repairing the lung epithelial barrier, maintenance of homeostasis and proliferation of lung epithelial cells to overcome IFN-I-mediated imunopathology [6/n]
5. Using two elegant transgenic mouse models: NAM-DTR and IFNAR-CKO mice - Yeung, Damani-Yokota & Khanna et al show that NAMs mitigate SARS lethality via type 1 interferon signaling. IFNAR1 expression on NAMs functions by sensing of type 1 IFNS (IFNa/b) as well as a survival switch for maintenance and proliferation of NAMs for their immunoregulatory functions to induce disease tolerance [5/n]
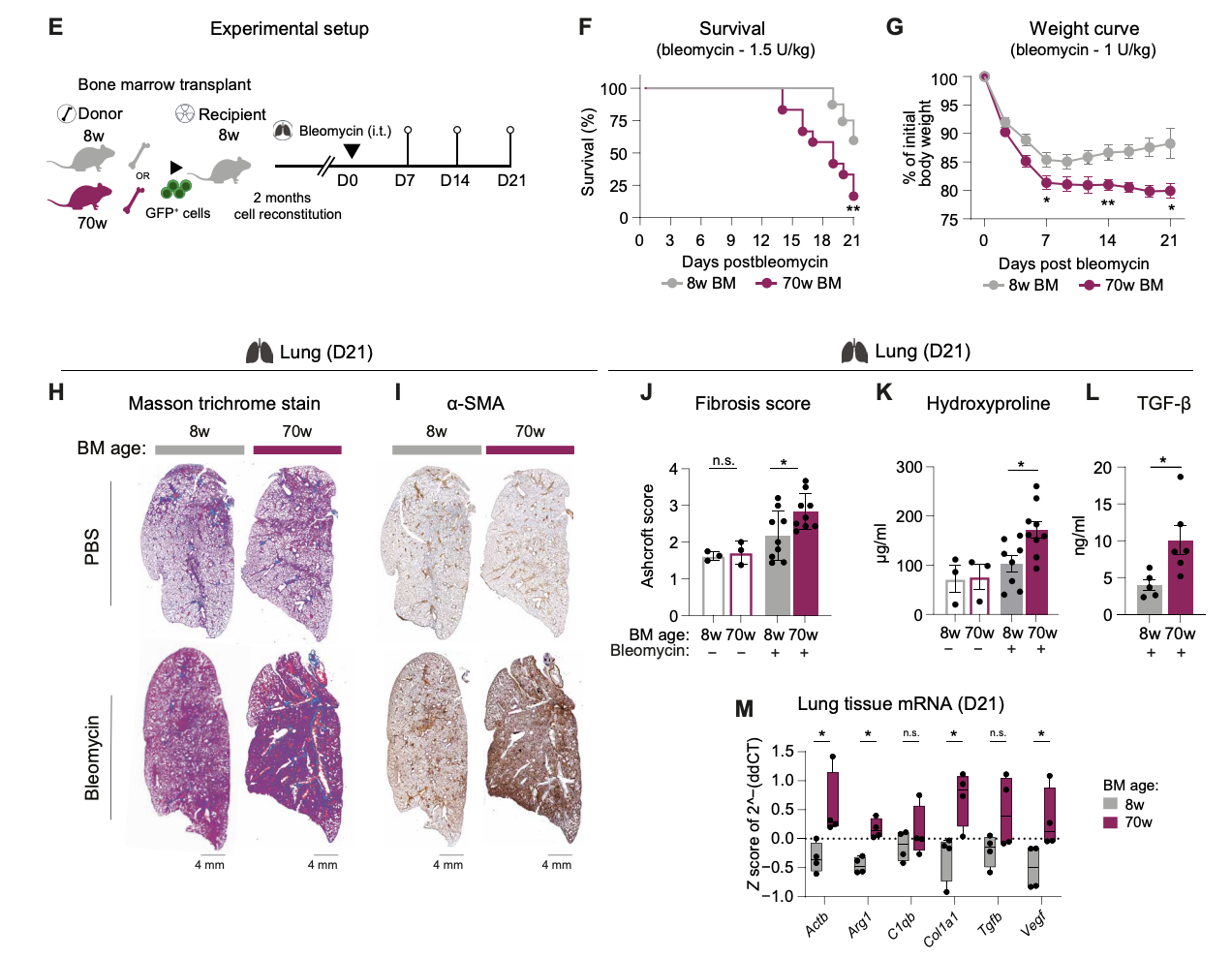
4. Using a fibrosis model in young vs aged mice, Farhat and Knapp show that an aged bone marrow autonomously produced more profibrotic Mo-AMs, had a reduced availability of Tregs-derived IL-10 causing exacerbated lung fibrosis. Very cool study showing the contribution of aged hematopoietic system in disease outcomes during lung fibrosis that relies on the Treg:IL-10 axis leading to the fibrotic phenotype of Mo-AMs.
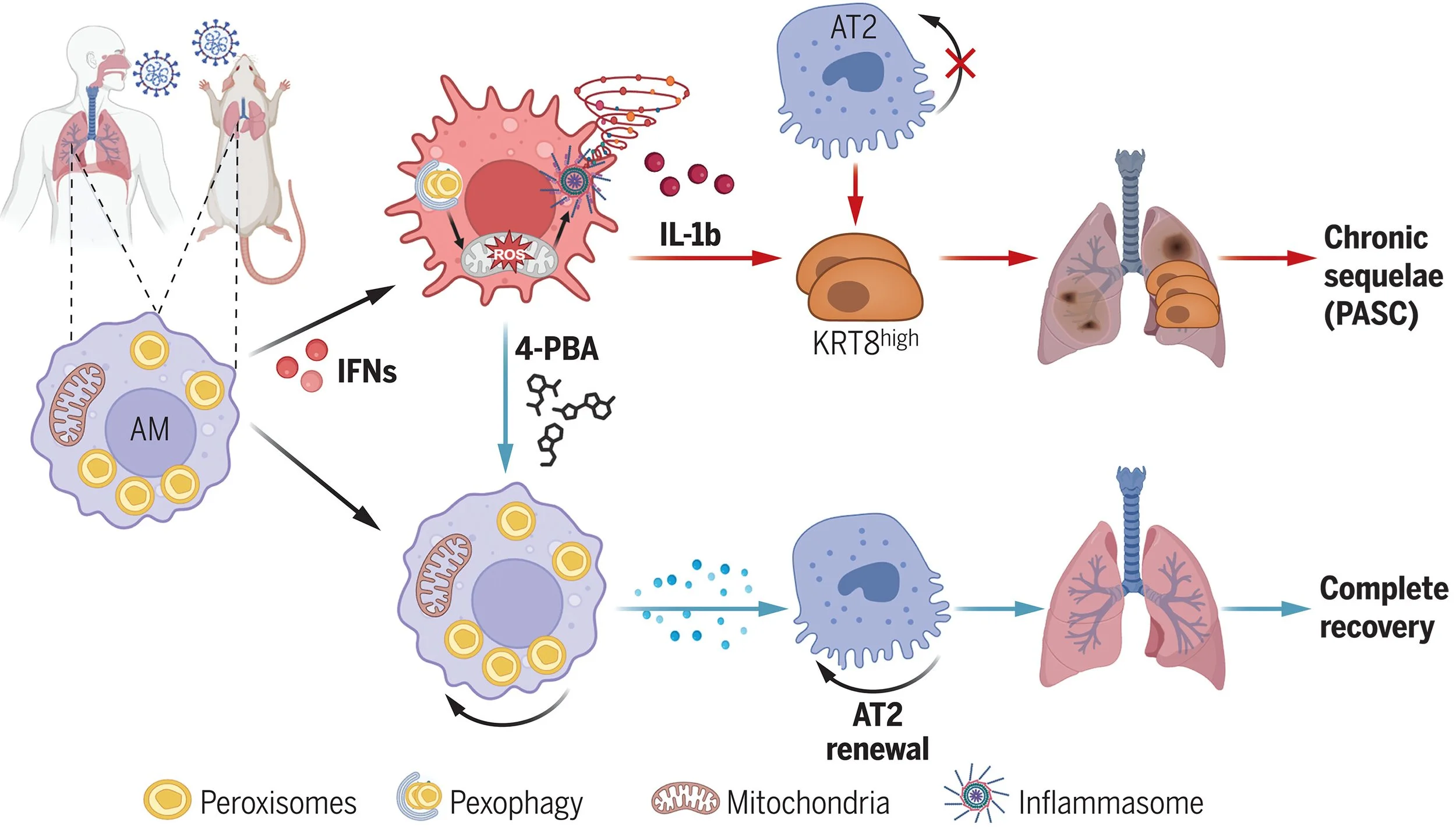
3. Using a comparative analyses of human and murine PASCs, Xiaoqin Wei and Jie Sun’s group at UVA report that sever COVID-19 causes disruption of peroxisomes (small membrane bound structures) in alveolar macrophages causing impaired lung repair, increased inflammation and chronic fibrosis.
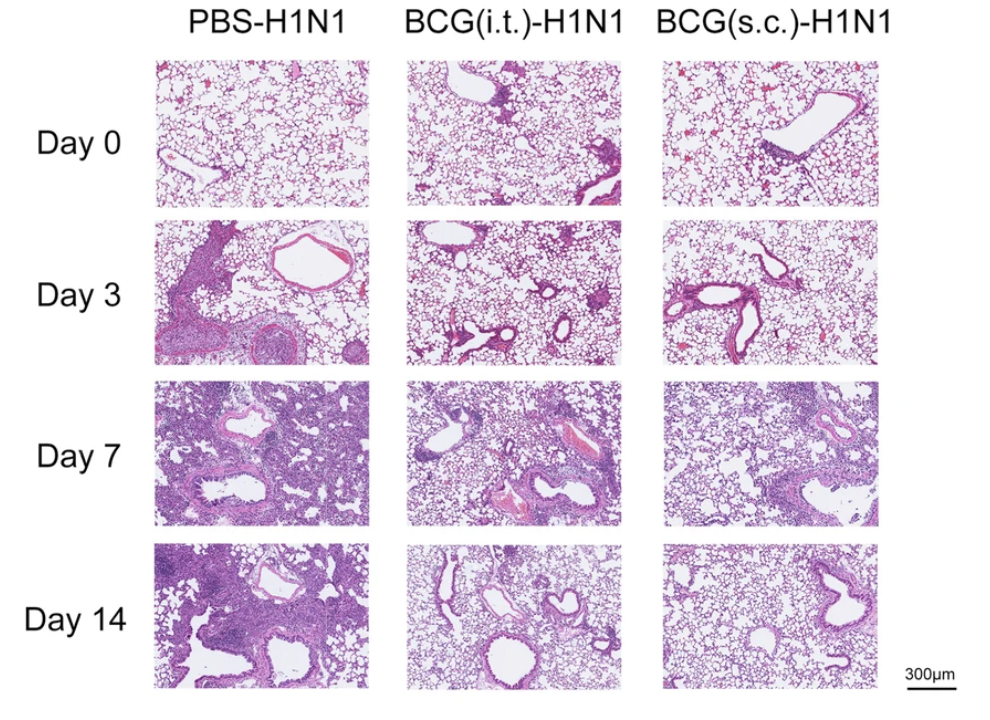
2. Dou Yu and Shuo Wang show that subcutaneous BCG vaccination induces MHCII+ ILC1 via TLR2 signaling, activate CD4+ T cells to promote anti-flu protection and immune response. Another evidence of skin:lung axis study.
1. Nargis Khan and Maz Divangahi show that β-glucan reprograms hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in the bone marrow to generate ‘regulatory’ neutrophils which are required for promoting disease tolerance and lung tissue integrity against IAV challenge.
Commentary:
This study is brilliant for so many reasons. Most of Maz’s papers, including this one, are great examples of papers that go above and beyond to present data from a variety of viewpoints to show the phenotype and really tug at the central hypothesis. What is really intriguing about this study is the discovery of regulatory neutrophil phenotype driven by modifications on the progenitors in the bone marrow decidedly from the beta glucan treatment. The broad implications of this study not only provide insights on the continuous BM replenishment through personal immune history, but the power of granulopoiesis and consequences on disease tolerance via mechanisms of central trained immunity.
2024
21. Rebecca Dodd and Tara Sutherland identify IL-13 as a modulator of the Hyaluronan (HA) matrix during lung challenge. Using Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb) model, authors link IL‐13‐mediated HA regulation to tissue repair pathways.
20. Sina Bohnacker and Julia Esser-Von Bieren published a beautiful study about identifying key roles of heGDH in immune evasion, parasite chronicity, and tissue repair during helminth infections (Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri, Hpb).
Representative iF image for hegDh (green), cD64 (magenta), and DaPi (blue) in the small intestine from a mouse in-fected with Hpb (4 days). White arrows indicate colocalization of hegDh and macrophages in the surroundings of l4 larvae (dashed circle).